What is Regenerative Agriculture?
We’re working to extend our sustainable agriculture programs beyond our own operations to create resilient and multifunctional landscapes throughout our entire watersheds.
We take a scientific approach to developing regenerative practices for agricultural production.

of owned land set aside to preserve biodiversity and protect wildlife
of our global product value, coming from our Pindeco and Bandeco farms, is sustainably grown, as certified by SCS Global Services
A holistic
approach
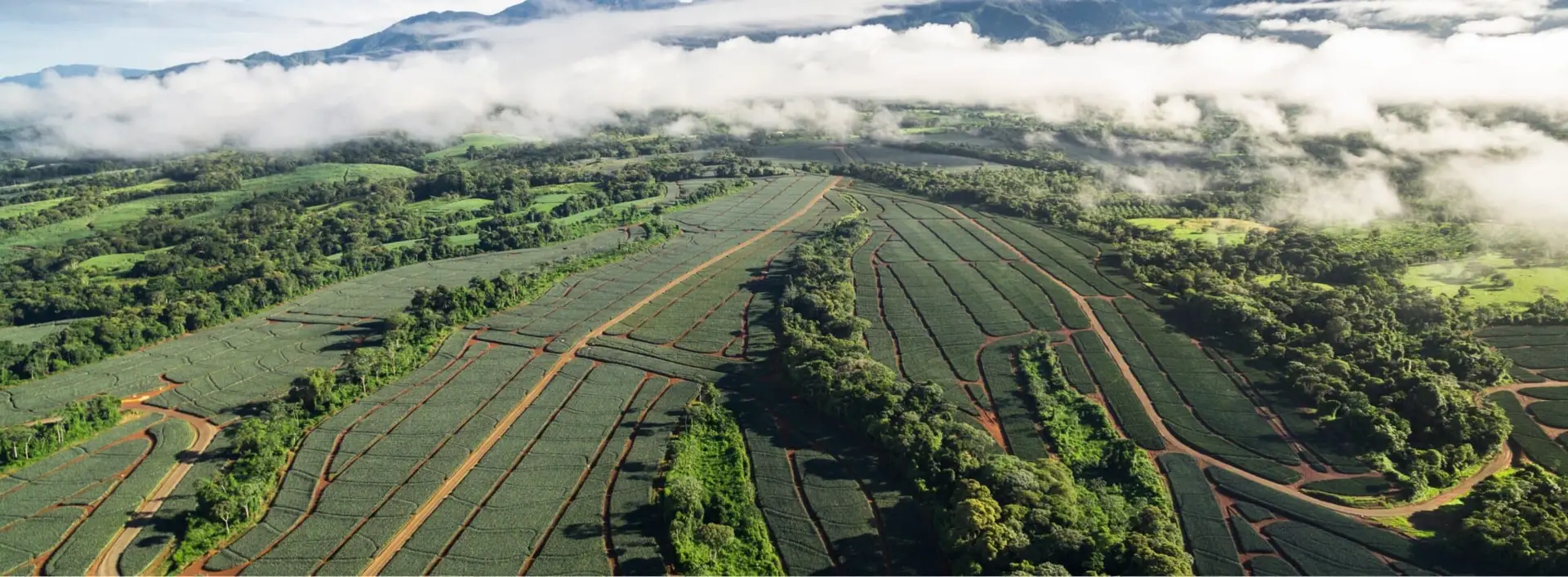
For us, regenerative agriculture is a holistic approach that includes increasing soil health, carbon sequestration, biodiversity, ecosystem health, and water availability and quality throughout our operations. It not only preserves the lands we grow in but helps to protect entire ecosystems and create resilient landscapes.
Soil health
Soil is where our crops meet the environment. Our scientists are working in the field to explore, validate, and implement best practices to address soil fertility, organic matter, soil structure, biodiversity of beneficial organisms, and soil erosion. These best practices are used in our own farms but we also share our knowledge with our associate growers.
Carbon sequestration
The forests in and around our operations are critical areas for sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. We harness the innate ability of our forests to achieve carbon neutrality by protecting forest ecosystems, reforesting new areas in our lands with native tree species, and involving and empowering our local communities through education and tree-planting activities.
Two of our largest operations—our pineapple (Pinedeco) and banana (Bandeco) farms in Costa Rica—are now certified carbon neutral by SCS Global Services.
Biodiversity
Ecosystem health
Our agricultural landscapes are functional ecosystems and we aim to provide products for consumers while conserving biodiversity. We set aside significant tracts of land to increase biodiversity and work to maximize ecosystem services, including carbon sequestration, pollination, erosion reduction, and improvements in water quality.
Water conservation
Climate change is one of the main reasons we need to reduce water use. We are working to improve our water monitoring capabilities and to reduce our water footprint by investing in upgrades of existing infrastructure to more efficient drip irrigation systems, maintenance programs that allow equipment and pipes to operate more efficiently, and systems to recycle and reuse water.
Relying on research and development
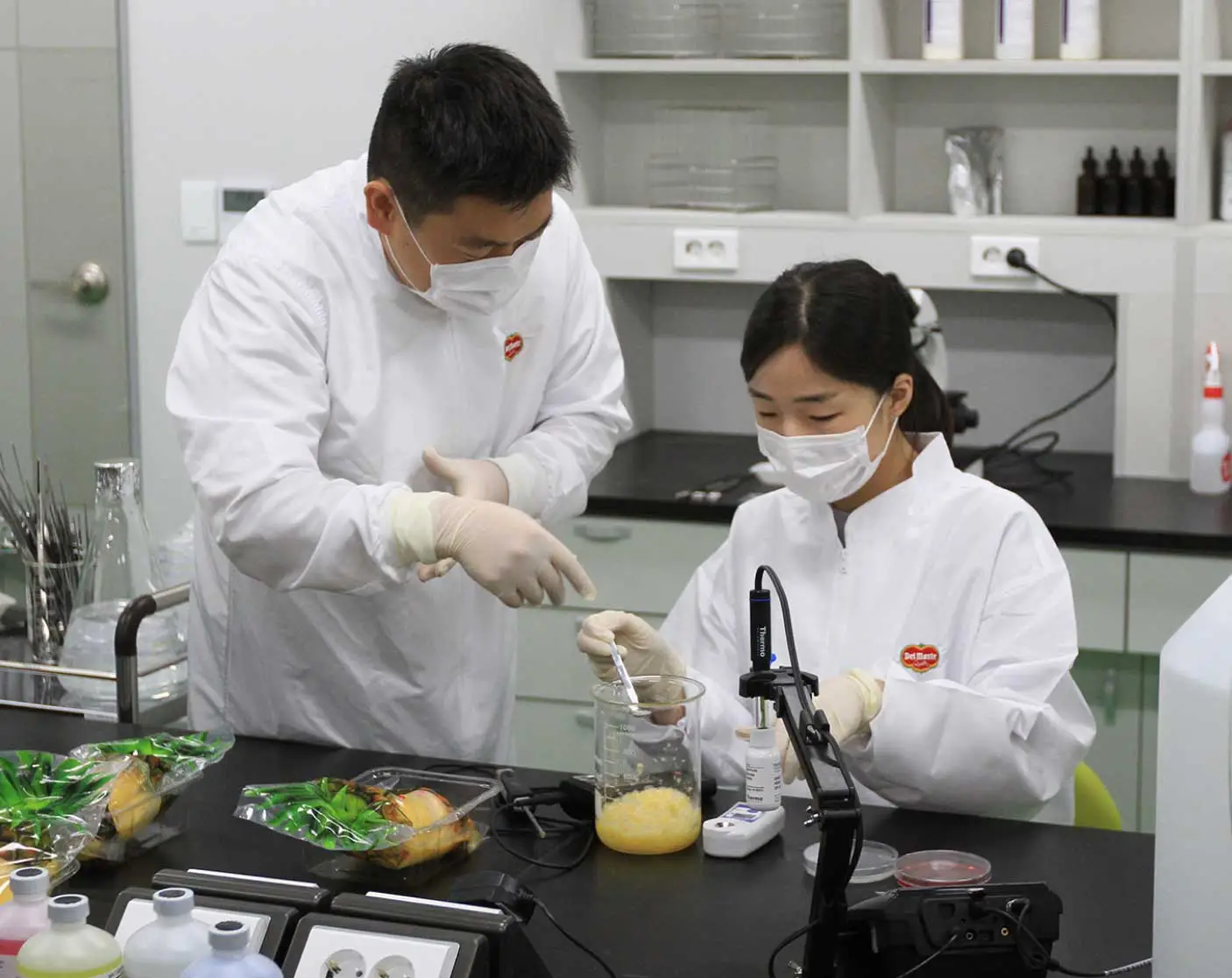

Smart farming
Smart farming allows us to optimize agricultural production while reducing environmental impacts.
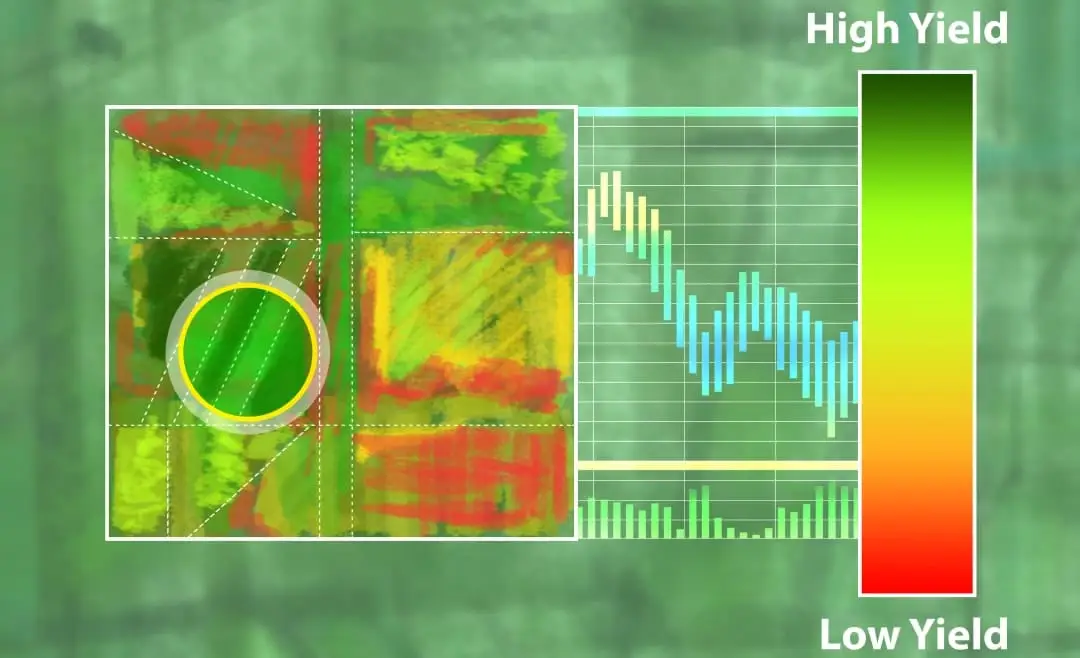
Digital yield maps
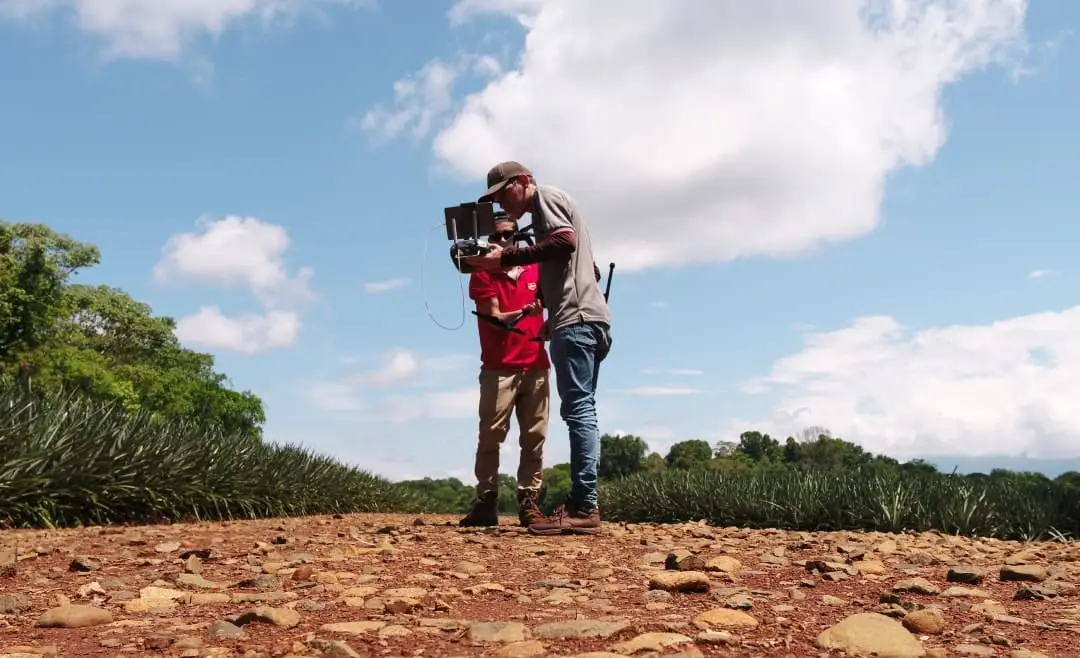

Drone usage

Read more about our sustainability efforts
